【tensorflow】RNN
🗓 2018年10月22日 📁 文章归类: 0x24_NLP
版权声明:本文作者是郭飞。转载随意,标明原文链接即可。
原文链接:https://www.guofei.site/2018/10/22/rnn.html
Why
- Why sequence models
- speech recognition
- Muscic generation
- sentiment classification
- DNA sequence analysis
- machine translation
- video activity recognition
- name entity recognition
- Why not standard network
- inputs, outputs can be diffent lenghths in different examples
- doesn’t share features learned across different pisitions of text
different types of RNN
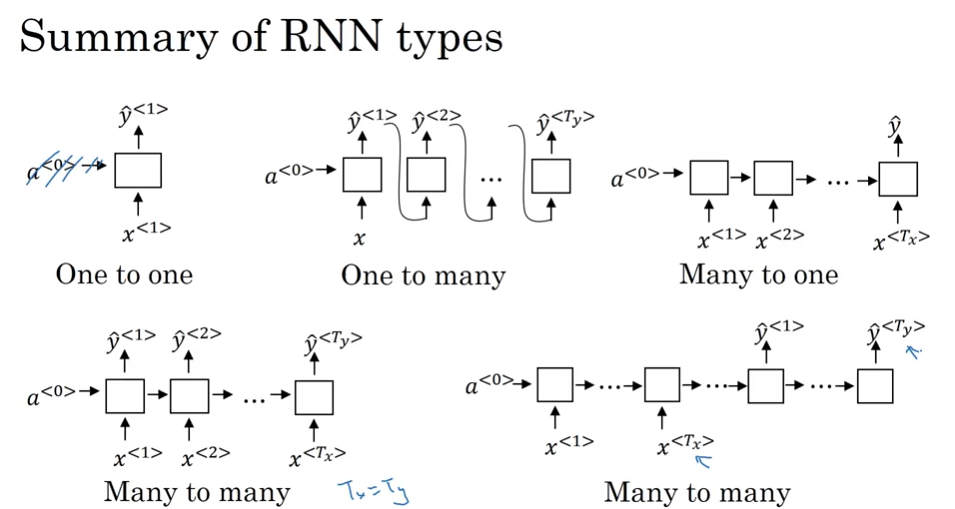
数据流向
train 过程
(画本子上了,有空补上)
sampling 生成
t时间依概率(这个概率是softmax的输出)进行采样,然后作为下一个$t+1$的输入$x^{<t+1>}=\hat y^{
- EOS 也加入 sampling
- 万一 sample 到 UNK,那么继续sample
- 还有一种是 character level language model(输入是大小写字母,空格标点等)
- 优点:不用担心 UNK
- 缺点:RNN太长了,导致效果不好,训练还费事。
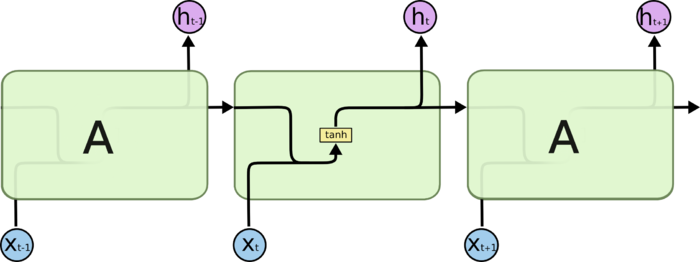
架构
如果把全联结网络表示为$y=\sigma(Ax)$,
那么RNN可以表示为$y=\sigma(By_{t-1}+Ax_t)$
different types of RNN:

1. 单个RNN层
tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(cell,inputs,sequence_length=None,initial_state=None,dtype=None,parallel_iterations=None,swap_memory=False,time_major=False,scope=None)
cell = tf.contrib.rnn.BasicRNNCell(num_units=rnn_size)
# x:[batch,n_inputs,len_input]
output, state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(cell, x, dtype=tf.float32)
# output:[batch,n_inputs,rnn_size]
# state:[batch,rnn_size]
# output是每一步的输出,state是最后一步的输出,因此state=output[:,-1,:]
weights, bias = cell.get_weights()
# weights:[len_input+rnn_size,rnn_size],因为每次的输入不仅有x,还有上次的输出h
# bias:[rnn_size]
2. deepRNN
下面是一个多隐藏层(deepRNN)
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
n_steps = 2
n_inputs = 3
n_neurons = 5
n_layers = 3
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_steps, n_inputs])
seq_length = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None])
layers = [tf.contrib.rnn.BasicRNNCell(num_units=n_neurons,
activation=tf.nn.relu)
for layer in range(n_layers)]
multi_layer_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.MultiRNNCell(layers)
outputs, states = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(multi_layer_cell, X, dtype=tf.float32, sequence_length=seq_length)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
X_batch = np.array([
# step 0 step 1
[[0, 1, 2], [9, 8, 7]], # instance 1
[[3, 4, 5], [0, 0, 0]], # instance 2 (padded with zero vectors)
[[6, 7, 8], [6, 5, 4]], # instance 3
[[9, 0, 1], [3, 2, 1]], # instance 4
])
seq_length_batch = np.array([2, 1, 2, 2])
with tf.Session() as sess:
init.run()
outputs_val, states_val = sess.run(
[outputs, states], feed_dict={X: X_batch, seq_length: seq_length_batch})
print("outputs_val.shape:", outputs, "states_val.shape:", states)
print("outputs_val:", outputs_val, "states_val:", states_val)
output:
outputs_val.shape:
Tensor("rnn/transpose_1:0", shape=(?, 2, 5), dtype=float32)
states_val.shape:
(<tf.Tensor 'rnn/while/Exit_3:0' shape=(?, 5) dtype=float32>,
<tf.Tensor 'rnn/while/Exit_4:0' shape=(?, 5) dtype=float32>,
<tf.Tensor 'rnn/while/Exit_5:0' shape=(?, 5) dtype=float32>)
总结下来,就是下面两句话:
outputs是 最后一层每个step 的输出
states是 每一层的最后那个step 的输出
3. Bidirectional RNN
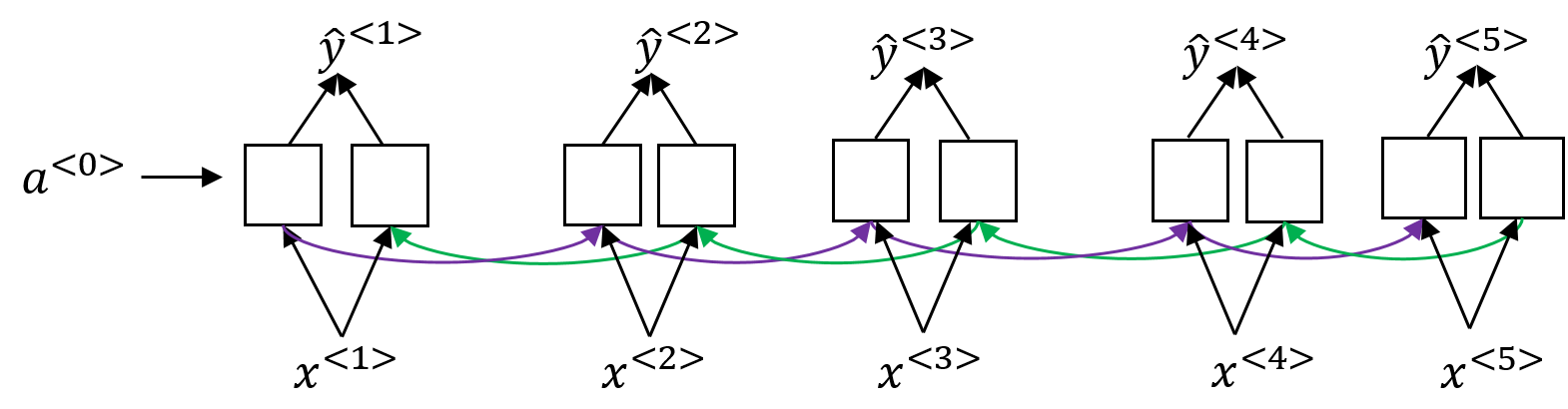
其它
3. LSTM
outputs仍然是 最后一层每个step 的输出
states由2个tensor组成:一个是c表示长期记忆信息,一个是h表示短期记忆信息。并且LSTM最后一个step的输出是H
LSTMStateTuple(c=<tf.Tensor 'rnn/while/Exit_3:0' shape=(128, 128) dtype=float32>, h=<tf.Tensor 'rnn/while/Exit_4:0' shape=(128, 128) dtype=float32>)
4. Dropout
实现
step1:导入包和数据
导入包,加载数据,并对文本进行清洗
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
epochs = 20
batch_size = 250
max_sequence_length = 25
rnn_size = 10
embedding_size = 50
min_word_frequency = 10
# %%
import pandas as pd
import re
df = pd.read_csv('http://www.guofei.site/datasets_for_ml/SMSSpamCollection/SMSSpamCollection.csv', sep='\t', header=None, names=['label', 'sentences'])
regex = re.compile('[a-zA-Z]{1,}')
text_data_train = [regex.findall(sentence.lower()) for sentence in df.sentences]
text_data_train = [' '.join(words) for words in text_data_train]
text_data_target = ((df.label == 'ham') * 1).values
step2:word转num
vocab_processor = tf.contrib.learn.preprocessing.VocabularyProcessor(max_sequence_length,
min_frequency=10)
text_processed = np.array(list(vocab_processor.fit_transform(text_data_train)))
vocab_size = len(vocab_processor.vocabulary_)
step3:train test split
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(text_processed, text_data_target, test_size=0.2)
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test
step4:构建网络
x_data = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None, max_sequence_length])
y_output = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None])
dropout_keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
embedding_mat = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([vocab_size, embedding_size], -1.0, 1.0))
# embedding_mat: [batch,len_input]
# (927*50)
embedding_output = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embedding_mat, x_data)
# embedding_output: [batch,num_inputs,len_input]
# ([?,25,50])
cell = tf.contrib.rnn.BasicRNNCell(num_units=rnn_size)
output, state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(cell, embedding_output, dtype=tf.float32)
# output: [batch,num_inputs,rnn_size],state:[batch,rnn_size]
# ([batch,25,10],state:[batch,10])
last=tf.nn.dropout(state,dropout_keep_prob)
# last = tf.nn.dropout(output[:, -1, :], dropout_keep_prob) # 等价写法
# 下面是全连接层
weight = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([rnn_size, 2], stddev=0.1))
bias = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[2]))
logits_out = tf.matmul(last, weight) + bias
# Loss function
losses = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits_out, labels=y_output)
loss = tf.reduce_mean(losses)
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(tf.argmax(logits_out, 1), tf.cast(y_output, tf.int64)), tf.float32))
optimizer = tf.train.RMSPropOptimizer(learning_rate=0.0005)
train_step = optimizer.minimize(loss)
step5: 进行训练
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
train_loss = []
test_loss = []
train_accuracy = []
test_accuracy = []
# Start training
for epoch in range(epochs):
# Shuffle training data
shuffled_ix = np.random.permutation(np.arange(len(x_train)))
x_train = x_train[shuffled_ix]
y_train = y_train[shuffled_ix]
num_batches = int(len(x_train) / batch_size) + 1
for i in range(num_batches):
# Select train data
min_ix = i * batch_size
max_ix = np.min([len(x_train), ((i + 1) * batch_size)])
x_train_batch = x_train[min_ix:max_ix]
y_train_batch = y_train[min_ix:max_ix]
# Run train step
train_dict = {x_data: x_train_batch, y_output: y_train_batch, dropout_keep_prob: 0.5}
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict=train_dict)
# Run loss and accuracy for training
temp_train_loss, temp_train_acc = sess.run([loss, accuracy], feed_dict=train_dict)
train_loss.append(temp_train_loss)
train_accuracy.append(temp_train_acc)
# Run Eval Step
test_dict = {x_data: x_test, y_output: y_test, dropout_keep_prob: 1.0}
temp_test_loss, temp_test_acc = sess.run([loss, accuracy], feed_dict=test_dict)
test_loss.append(temp_test_loss)
test_accuracy.append(temp_test_acc)
print('Epoch: {}, Test Loss: {:.2}, Test Acc: {:.2}'.format(epoch + 1, temp_test_loss, temp_test_acc))
step6:画loss图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Plot loss over time
epoch_seq = np.arange(1, epochs + 1)
plt.plot(epoch_seq, train_loss, 'k--', label='Train Set')
plt.plot(epoch_seq, test_loss, 'r-', label='Test Set')
plt.title('Softmax Loss')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Softmax Loss')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.show()
# Plot accuracy over time
plt.plot(epoch_seq, train_accuracy, 'k--', label='Train Set')
plt.plot(epoch_seq, test_accuracy, 'r-', label='Test Set')
plt.title('Test Accuracy')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.show()
(如果使用RNN模型,强烈建议对全部训练集进行多次训练)
参考文献
【美】尼克麦克卢尔:《TensorFlow机器学习实战指南》
https://blog.csdn.net/junjun150013652/article/details/81331448
您的支持将鼓励我继续创作!
