【dummies】虚拟变量回归
🗓 2016年05月04日 📁 文章归类: 0x21_有监督学习
版权声明:本文作者是郭飞。转载随意,标明原文链接即可。
原文链接:https://www.guofei.site/2016/05/04/DummyVariableRegression.html
虚拟变量回归,又叫做哑变量回归(Dummy Variable Regression Models)
虚拟变量
又叫做哑变量,Dummy Variable
指的是取值0或1的变量,用来代表类别
一个分类量有k个类别时,需要引入k-1个虚拟变量
例如:
要研究大学生学习成绩和收入之间的关系,考虑到4个年级的情况未必相同,因此把年级也放到Dependent Variables里面,对年级这样构造:
$Y=a_0+a_1D_1+a_2D_2+a_3D_3+a_4X+\epsilon$
其中,$D_1$=1是大一,否则为0.
$D_2$代表大二,否则为0.
$D_3$代表大三,否则为0.
注意1
为什么表示多个类时,要用多个0-1变量,而不用一个0,1,2,3变量?
答:
如果用0,1,2,3 那么就只能以连续变量理解这个变量,认为这个变量既有大小又有刻度
注意2
为什么一个分类量有k个类别时,引入k-1个Dummy Variables, 而不是k个?
答:
如果引入k个Dummy Variables, 将会有完全的多重共线性
$D_1+D_2+D_3+D_4 \equiv 1$
加法模型
$Y=a_1+a_2D_1+a_3D_2+bX+u$
模型解释
例如,Y代表啤酒销售量,X代表收入。
$D_1=1$代表夏季,0代表冬季
$D_2=1$代表城市,0代表农村
模型是这样的:
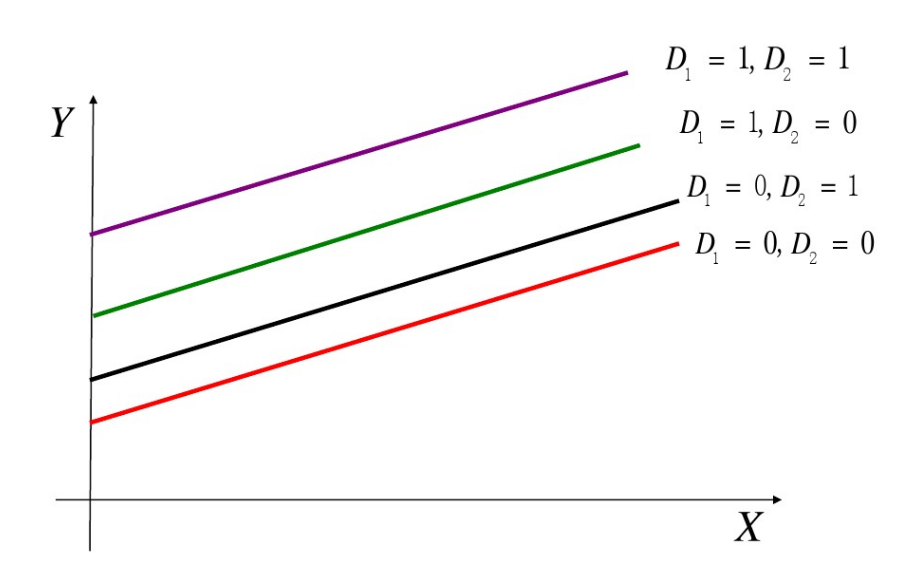
其特点是斜率不变
加法模型的变种
引入交互作用
$Y=a_1+a_2D_1+a_3D_2+a_4D_1D_2+bX+u$
乘法模型
$Y=a_1+a_2D+b_1X+b_2DX+u$
特点是截距斜率都变化
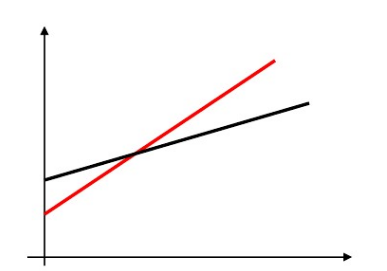
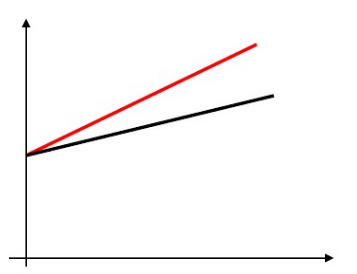
乘法模型的变种
$Y=a_1+b_1X+b_2DX+u$
分段模型
$Y=a_0+b_1X+b_2(X-X^* )D+u$
其中,
\(D=\left \{ \begin{array}{ccc}
1&X>=X*\\
0&X<X^*
\end{array}\right.\)
图像是一个折线(两条共点的线段)
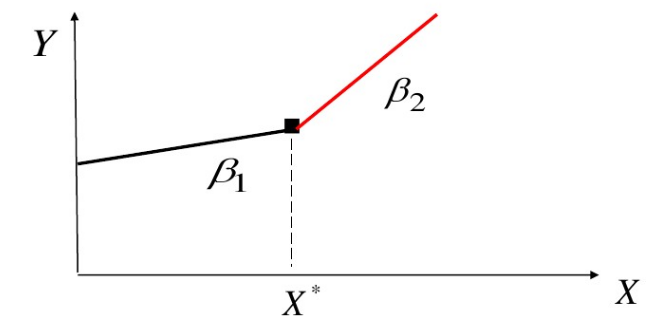
其它虚拟变量回归模型
Dummy Dependent Variables
dependent Variables是dummy,而independent是quantitative Variables。
这实际上是分类模型,有大量的classifier模型可以用,例如决策树模型,SVM等等
用OLS做这个模型,被称为Linear probability model
Linear probability model有诸多缺点,wikipedia总结的很好:
Some problems are inherent in the LPM model:
- The regression line will not be a well-fitted one and hence measures of significance, such as R2, will not be reliable.
- Models that are analyzed using the LPM approach will have heteroscedastic disturbances.
- The error term will have a non-normal distribution.
- The LPM may give predicted values of the dependent variable that are greater than 1 or less than 0. This will be difficult to interpret as the predicted values are intended to be probabilities, which must lie between 0 and 1.
- There might exist a non-linear relationship between the variables of the LPM model, in which case, the linear regression will not fit the data accurately.
为了规避这些缺点,改进为logit regression,见于我的另一篇文章逻辑回归
大名鼎鼎的logit regression本质上可以归类为Dummy Variable Regression
模型检验
- 对整个模型的检验(F检验) H0:$b_1=b_2=…=0$
- 对系数的检验(t检验) H0:$b_j=0$
您的支持将鼓励我继续创作!
